What is THCC (Tetrahydrocannabiorcol)? Uses & Benefits

If you follow cannabis-related news, you have probably recently heard about tetrahydrocannabiorcol (THCC), a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis and hemp pollen.
Despite its name, THCC is more similar to CBD than it is to THC. It’s non-psychoactive and targets more or less the same cannabinoid receptors as CBD, CBC, and CBG.
So, what is THCC? Here’s everything you need to know about this unique new cannabinoid.
What is THCC?
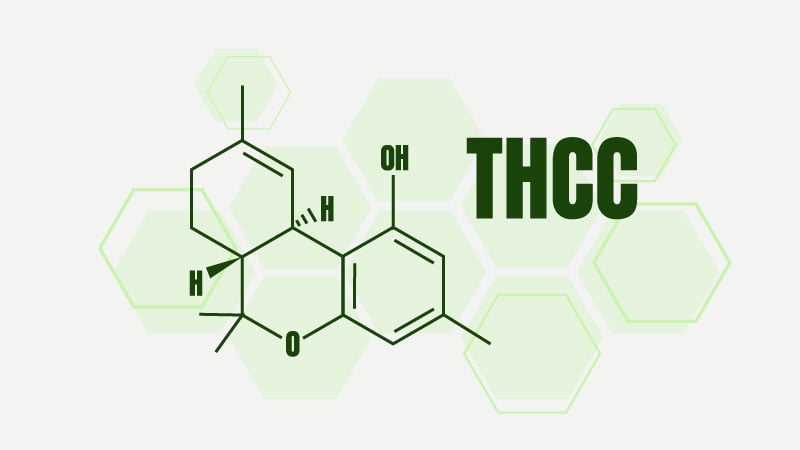
THCC is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in both cannabis plant varieties — hemp plants and marijuana.
It’s part of a broad category of cannabinoids that share a similar chemical structure to THC and are created through similar chemical processes as a cannabis or hemp plant matures. From a medicinal chemistry angle, THCC is part of the “tetrahydrocannabiorcolic” group.
From a molecular perspective, THCC is nearly identical to THC. The difference is as subtle as three missing carbon atoms — but this makes a big difference in the effect profiles of these cannabinoids.
THCC is unable to activate the CB1 receptors — which is what THC appears to exert its psychoactive effects on.
Instead, THCC appears to work in much the same way as CBD.
THCC appears to upregulate the body’s naturally occurring endocannabinoids and interacts with a parallel system of receptors called the TRP channels.
With that said, more research is needed to uncover the potential health benefits of THCC.
Is THCC Synthetic?
No, THCC is found naturally in the cannabis plant.
THCC is a phytocannabinoid, that is, a cannabinoid that naturally occurs in marijuana and hemp plants.
Specifically, THCC appears in cannabis and hemp pollen, unlike THC, which is found in the resin produced on the female flowers.
THCC occurs naturally and exists independently from humans unlike synthetic cannabinoids that are created in a lab.
Where Does THCC Come From?

Many cannabinoids — including THC and THCC — begin their life as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA).
As the plant grows, CBGA undergoes one of several enzymatic reactions that convert it to various acidic molecules that are precursors to the biologically active compounds humans like to consume, like THC and THCC, as two examples.
The precursor molecule to THCC is called tetrahydrocannabiorcolic acid (THCCA), and it gets converted to THCC over the cannabis or hemp plant’s maturation cycle through a process called decarboxylation.
Companies extract THCC from either marijuana or hemp pollen and concentrate it the same way other cannabinoids are concentrated. This makes them easier to use and eliminates unnecessary components like amino acids, proteins, fibers, and plant cell structures.
Is THCC Legal?
Since THCC isn’t the same as THC, it’s rarely mentioned explicitly in legal texts. However, hemp plant derivatives with below 0.3% delta 9 THC are generally legal, which also likely covers THCC in many jurisdictions. Yet the Drug Enforcement Administration lumps anything “THC-like” into a grey area.
Because THCC is inherently non-psychoactive and found in hemp pollen, many interpret it as legal under the 2018 Farm Bill. But state laws vary, and local agencies may see it as “THC products” if they’re unfamiliar with the nuance of THCC’s legal status. The truth is, laws aren’t always up-to-date with other cannabinoids like THCC. That said, always verify local regulations before purchasing or using THCC.
States where THCC is likely illegal:
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Iowa
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Mississippi
- Montana
- Nevada
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Utah
- Vermont
- Washington
These laws change all the time, so make sure you do your research before you buy THCC.
We do our best to avoid shipping to states where our products are prohibited, but it’s up to you to make sure you’re not ordering products illegally in your state.
THCC vs. THC: What’s the Difference?
From their names, you can probably tell that THC and THCC are similar molecules, but they aren’t identical.
THC and THC-like molecules have an important molecular feature called an alkyl side chain that governs their biological activity. The longer this side chain, the stronger the psychoactive effects.
Delta 8, 9, and 10 THC all have a side chain of 5-carbons long, while THCC only has one.
Other forms of THC include THCV (3 carbons, mildly psychoactive), THCP (7 carbons, highly psychoactive).
In terms of effects, THCC is most similar to CBD. It has a pleasant, relaxing effect similar to the experienced felt by using delta 8 THC but without any psychoactivity.
THCC in Medicinal Chemistry & Cannabis Research
Ongoing cannabis research suggests each cannabinoid has unique roles in human health. With marijuana legalization expanding globally, scientists have greater freedom to investigate lesser-known cannabinoids like THCC.
Early studies highlight THCC’s possible involvement in homeostasis, pain modulation, and immune function. However, these remain hypotheses until more robust trials confirm them.
Pharmacologically, THCC may exert mild anti-inflammatory effects or help with stress management by targeting TRP channels (transient receptor potential channels) and possibly influencing the ECS (endocannabinoid system).
Some researchers in medicinal chemistry see THCC as a candidate for future drug formulations that avoid sedation or cognitive impairment typically linked with THC. We’ll likely see more data as research on medical marijuana advances and restrictions on illegal drug research loosen.
How Does THCC Work?

THCC works through two primary systems — the endocannabinoid system and the TRP channels.
Let’s cover how each of these works in more detail.
Your body’s endocannabinoid system consists of two main receptors that interact with cannabinoids to produce the array of effects we experience when we consume THCC.
Cannabinoid receptors of type 1 (CB1) are primarily located in the central nervous system in the brain and spinal cord. They play a role in creating the euphoric and psychotropic effects of THC [2].
Cannabinoid receptors of type 2 (CB2) are primarily located in the peripheral nervous system in the organs and immune cells.
Unlike THC, THCC has virtually no affinity for CB1 or CB2 receptors, meaning it doesn’t produce a high and doesn’t have the same effects that THC does. It works the same way as CBD in this regard — boosting the effects of naturally occurring endocannabinoids like anandamide and 2-AG instead.
THCC also activates the body’s TRPA1 and other TRP receptors. These receptors are found on special gated ion channels on the cell wall. They play a critical role in our perception of pain, regulation of temperature and may even be involved with nerve cell regeneration.
Does THCC Get You High?
No. Unlike THC, THCC has a much smaller alkyl chain and has virtually no interaction with the body’s CB1 receptors, meaning it doesn’t have any psychoactive properties.
No matter how much of this cannabinoid you take, you’re not going to feel high like you do with other THC or cannabis products.
How to Use THCC
THCC is typically found in trace amounts, so it’s hard to source alone. Some specialized labs isolate THCC from pollen, creating extracts or tinctures. Pure THCC is virtually impossible to find on dispensary shelves or mainstream markets. More likely, you’ll see “full-spectrum hemp pollen extract” that boasts THCC content.
Much like the oral administration of CBD or CBG, if you get THCC, you’d incorporate it as drops under the tongue or capsules. The synergy with cannabinoid receptors and minimal sedation makes it appealing for functional daytime relief. If you see a “THC extract” or “oral THC supplement” labeled with THCC, ensure it’s tested for purity before making a purchase.
Do note too that we need more research on THCC and its potential in medical cannabis use. There’s also not enough data on its median lethal dose.
Key Takeaways: What is THCC?
THCC is one of many naturally occurring compounds found in cannabis and hemp plants.
Unlike THC, THCC doesn’t produce a high and interacts with the body through entirely different pathways. It’s much more similar to CBD than it is to delta 8, 9, or 10 THC.
As marijuana legalization evolves, lesser-known cannabinoids may become more accessible. THCC might be the next frontier in medical marijuana or consumer hemp markets, prized for potential benefits without the side effects. For now, verifying product purity and ensuring compliance with local laws is a must.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will THCC Show Up on a Drug Test?
It’s unlikely but not impossible. Standard drug tests look for THC metabolites, not THCC. Because THCC has a different chemical makeup, normal urine or saliva panel tests probably won’t detect it.
However, labs regularly update testing methods. If they specifically include tetrahydrocannabiorcol in a screening, it might flag you. Until more details are out, it’s best to be cautious.
2. Is THCC Regulated by the DEA?
Not explicitly, but it can be a gray area. Federal law mainly targets delta 9 THC and synthetic variations, leaving THCC mostly off the radar. However, the DEA can interpret broad definitions of “illegal drug” or “THC extract” to include THCC if they want to. For now, it’s usually lumped with other hemp plant derivatives which is generally believed to be legal under the 2018 Farm Bill.
3. Why Haven’t I Seen THCC in Cannabis Dispensaries?
THCC it’s rare, and too little of the substance is made. It’s not as common as delta 9 THC or CBD, appearing in very small quantities in cannabis plant pollen. Most manufacturers don’t have the technology or incentive to mass-produce it.
However, as marijuana legalization progresses and cannabis research expands, you might see THCC in specialized shops, but for now, it’s considered a niche cannabinoid.
4. What is the meaning of THCC?
THCC stands for tetrahydrocannabiorcol, a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found mainly in the cannabis or hemp pollen.
5. Where Can I Find High-Quality THCC Products?
THCC products are tough to find, especially since THCC isn’t mainstream and reliable sources can be very rare. However, online specialty vendors may be your best options.
Look for vendors offering third-party lab tests verifying purity, as synthetic cannabinoids or mislabeled extracts sometimes saturate the market. If local dispensaries don’t carry THCC, your best bet is an online retailer that transparently posts certificates of analysis, ensuring you’re not buying mislabeled or contaminated goods






